CONFUSION IN ROR - ROI - IRR - EIR
In finance, return on investment (ROI), also known as rate of return (ROR), rate of profit or sometimes just return is the ratio of money gained on an investment relative to the amount of money invested.
The amount of money gained may be referred to as interest, net profit/loss. The money invested may be referred to as the asset, capital, principal, stocks, claims, outstandings or the cost basis of the investment.
ROI = Net Profit / Investment
The amount of money gained may be referred to as interest, net profit/loss. The money invested may be referred to as the asset, capital, principal, stocks, claims, outstandings or the cost basis of the investment.
ROI = Net Profit / Investment
where
Net Profit = Gross Profit - Investment
Investment = Money invested + Outstandings + Stocks + Claims
ROI is usually expressed as a percentage rather than a fraction. ROI does not indicate how long an investment is held. However, ROI is most often stated as an annual or annualized rate of return, and it is most often stated for a calendar or fiscal year.
The internal rate of return (IRR) is a capital budgeting metric used by firms to decide whether they should make investments. It is an indicator of the efficiency or quality of an investment, as opposed to net present value (NPV), which indicates value or magnitude.
Simply, IRR is the rate of return that makes the net present value of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero. Generally speaking, the higher a project's internal rate of return, the more desirable it is to undertake the project.
The IRR is the annualized effective compounded return rate which can be earned on the invested capital, i.e., the yield on the investment. Put another way, the internal rate of return for an investment is the discount rate that makes the net present value of the investment's income stream total to zero.
A project is a good investment proposition if its IRR is greater than the rate of return that could be earned by alternate investments of equal risk (investing in other projects, buying bonds, even putting the money in a bank account). Thus, the IRR should be compared to any alternate costs of capital including an appropriate risk premium.
In general, if the IRR is greater than the project's cost of capital, or hurdle rate, the project will add value for the company.
In the context of savings and loans the IRR is also called effective interest rate.
Eventually, The IRR is the interest rate, also called the discount rate, that is required to bring the net present value (NPV) to zero. That is, the interest rate that would result in the present value of the capital investment, or cash outflow, being equal to the value of the total returns over time, or cash inflow.
Net Present Value :
Note that Initial investment is added to the calculation in excel formula. 'IRR' formula in Excel can be used to calculate the interest rate by selecting the investment and profits.
Net Profit = Gross Profit - Investment
Investment = Money invested + Outstandings + Stocks + Claims
ROI is usually expressed as a percentage rather than a fraction. ROI does not indicate how long an investment is held. However, ROI is most often stated as an annual or annualized rate of return, and it is most often stated for a calendar or fiscal year.
The internal rate of return (IRR) is a capital budgeting metric used by firms to decide whether they should make investments. It is an indicator of the efficiency or quality of an investment, as opposed to net present value (NPV), which indicates value or magnitude.
Simply, IRR is the rate of return that makes the net present value of all cash flows from a particular project equal to zero. Generally speaking, the higher a project's internal rate of return, the more desirable it is to undertake the project.
The IRR is the annualized effective compounded return rate which can be earned on the invested capital, i.e., the yield on the investment. Put another way, the internal rate of return for an investment is the discount rate that makes the net present value of the investment's income stream total to zero.
A project is a good investment proposition if its IRR is greater than the rate of return that could be earned by alternate investments of equal risk (investing in other projects, buying bonds, even putting the money in a bank account). Thus, the IRR should be compared to any alternate costs of capital including an appropriate risk premium.
In general, if the IRR is greater than the project's cost of capital, or hurdle rate, the project will add value for the company.
In the context of savings and loans the IRR is also called effective interest rate.
Eventually, The IRR is the interest rate, also called the discount rate, that is required to bring the net present value (NPV) to zero. That is, the interest rate that would result in the present value of the capital investment, or cash outflow, being equal to the value of the total returns over time, or cash inflow.
Net Present Value :
Note that Initial investment is added to the calculation in excel formula. 'IRR' formula in Excel can be used to calculate the interest rate by selecting the investment and profits.
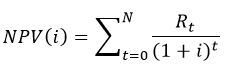
Nice and informative post.
YanıtlaSilReal Estate Financial Modeling
Waterfall Modeling